For information about the Schwarzchild radius, click here.
The Mass Luminosity Relationship applies only to main sequence stars – those stars which produce energy by fusing hydrogen into helium.
The amount of mass in a main sequence star affects many of its properties.
Generally speaking, if we are comparing 2 stars, the star with the greater mass will have:
- Higher Luminosity (and brighter absolute magnitude)
- Larger Radius
- Hotter Temperature
- A shorter lifetime and a more violent “death”
- A bluer color, and a “bluer” spectral type
Let’s first discuss how mass affects luminosity.
Effect of Star Mass On Luminosity
There is an equation that relates star mass and luminosity.
That equation is not an exact rule but it provides a good approximation.
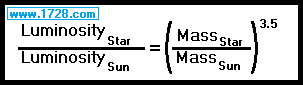

Absolute Magnitude = 4.83 ⚊2.5 • 1.6702458531
Absolute Magnitude = 4.83 ⚊4.1756146328
Absolute Magnitude = 0.6543853673
Effect of Star Mass On Radius
It makes sense that if a star has more mass, it will have a bigger radius.
In fact, here are the equations for calculating a star’s radius based on its mass.
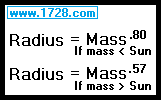
Where radius and mass are based on the Sun = 1.
and a star with twice the mass of the Sun will have a radius of 2.57 = 1.48.
Effect of Star Mass On Temperature
The star with the higher mass will have a higher surface temperature.
You have probably seen the following equation in many web pages and books:
A more appropriate equation is:
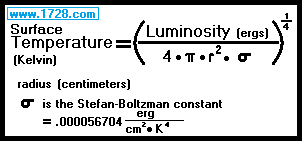
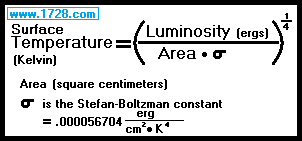
Sun’s Luminosity = 3.828 x 10³³ ergs.
Sun’s Surface Area = 6.09421 x 10²² square centimeters.
Effect of Star Mass On Longevity
It would seem common sense that if a star had higher mass, it should live longer but this is not the case.
The more massive a star becomes, its greater gravity requires higher temperatures and pressures to prevent gravitational collapse. The energy required for this causes the star to use up fuel at a rather furious rate.
So, a star that has 10 times the mass of the Sun has 10 times the fuel. However, as we know from the mass luminosity formula, the star will be consuming fuel at a rate equal to its mass to the 3.5 power.
Combining these two factors, a star’s mass will decrease (or increase) its lifetime by a factor of [mass] 2.5.
Knowing that the Sun will have a lifetime of 10 billion years, we can come up with this formula:
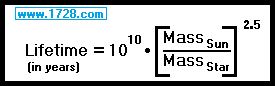
| Mass | Years | Mass | Years | Mass | Years | Mass | Years |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.080 | 5,500,000,000,000 | 0.50 | 57,000,000,000 | 2.50 | 1,000,000,000 | 20.00 | 5,600,000 |
| 0.100 | 3,200,000,000,000 | 0.75 | 21,000,000,000 | 3.00 | 640,000,000 | 25.00 | 3,200,000 |
| 0.125 | 1,800,000,000,000 | 1.00 | 10,000,000,000 | 4.00 | 310,000,000 | 40.00 | 990,000 |
| 0.150 | 1,100,000,000,000 | 1.25 | 5,700,000,000 | 5.00 | 180,000,000 | 50.00 | 570,000 |
| 0.200 | 560,000,000,000 | 1.50 | 3,600,000,000 | 10.00 | 32,000,000 | 100.00 | 100,000 |
| 0.250 | 320,000,000,000 | 2.00 | 1,800,000,000 | 12.50 | 18,000,000 | 150.00 | 36,000 |
A more massive star has a shorter lifetime and a more violent death than a lower mass star.
The lowest possible mass of a star is about .08 the mass of the Sun.
Depending on the star’s mass, we have made a table showing how each type of star ages.
| Mass | Evolves Into ****************************************************************** |
|---|---|
| 0.08 to .50 | After Hydrogen to Helium fusion ends, it becomes a white dwarf. |
| > 0.50 and < 1.5 | Hydrogen to Helium fusion ends then star gets larger, becoming a red giant, eventually forming a planetary nebula, then becomes a white dwarf. |
| 1.5 and < 3.2 | Becomes a red super-giant then becomes a supernova and finally forms a neutron star. |
| >= 3.2 | Becomes a red super-giant then becomes a supernova and finally forms a black hole. |
.08 Mass of the Sun = 1.6 x 1029 kg
Mass of the Sun = 2.0 x 1030 kg
Effect of Star Mass On Spectral Type and Color
This can easily be presented as a table.
| Mass | Spectral Type |
Color |
|---|---|---|
| >=16 | O | blue |
| 2.10 to 16 | B | blue white |
| 1.40 to 2.10 | A | white |
| 1.04 to 1.40 | F | yellow white |
| .80 to 1.04 | G | yellow |
| .45 to .80 | K | orange |
| .08 to .45 | M | red |